Gallbladder Function
The gallbladder is a small, pear-shaped organ located in the upper right abdomen in the area between the chest and hips, right below the liver. It is a place where are bodies store bile from the liver. An abnormal functioning gallbladder will produce something called gallstones which can be chronic and extremely painful. Here is what you need to know about gallstones.
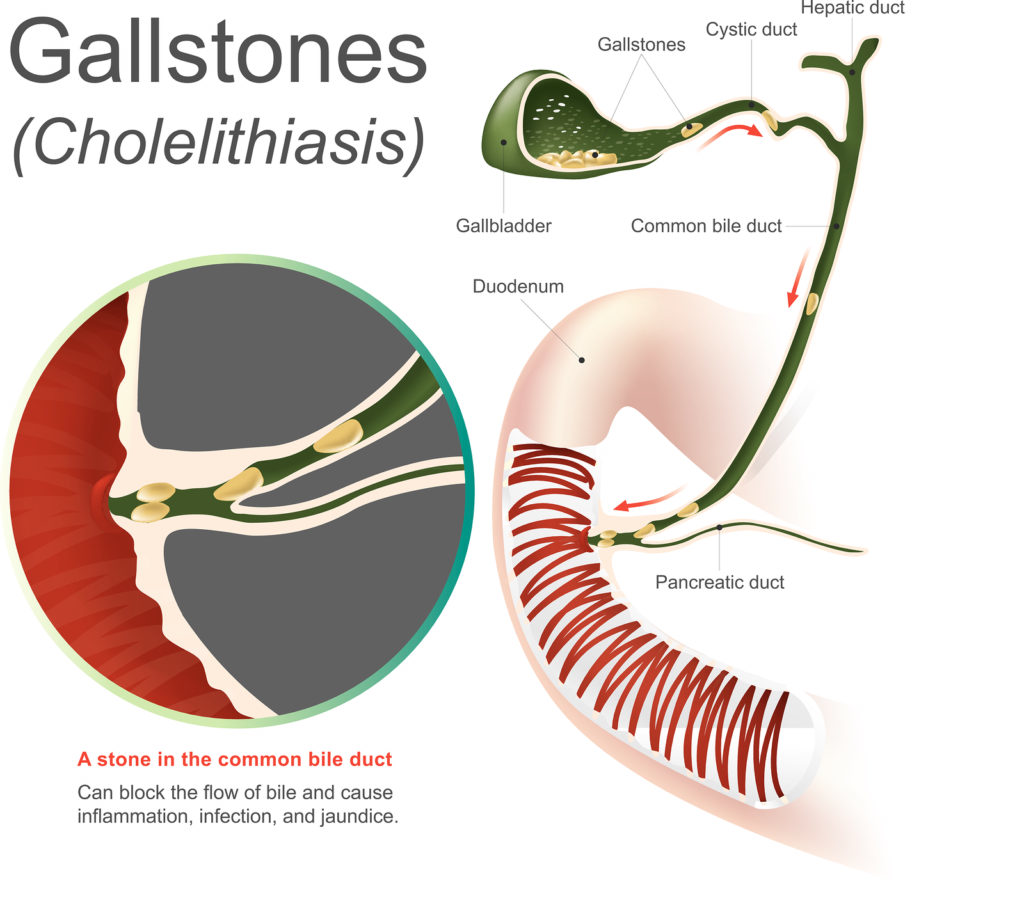
Gallstones
Gallstones are hard fragments that develop in the gallbladder made of protein, fat and minerals in our bodies. A gallbladder attack is caused by gallstones and can be a very painful, potentially dangerous medical condition. Did you know around 80 percent of people who have gallstones never have symptoms? (Minesh 2020)
The stones can be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball. The gallbladder can develop a single large gallstone, hundreds of tiny stones, or both small and large stones. When you eat fatty foods, bile is released from the gallbladder and liver into the intestines to break up the fat and absorb vitamins. When gallstones block the ducts of the biliary tract, it causes sudden pain in the upper right abdomen. But if gallstones are small enough, they leave the gallbladder through its draining ducts and then pass out of the body through the intestines.
Who Gets Gallstones?
Women between the ages of 20 and 60 are three times more likely to develop gallstones than men. Many women live their lives without knowing they have gallstones. The chances are much higher for women who have been pregnant multiple times, have a family history of gallstones, are of Hispanic or Native American descent, are obese, or have experienced rapid weight loss. People over the age of 40 are also more likely to develop gallstones than younger people. (ACG 2020)
Gallstones Symptoms
- Sudden pain in the upper right abdomen
- Sudden pain in the center of your abdomen
- Rapidly intensifying pain
- Back pain (between the shoulder blades)
- Pain in your right shoulder
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fever
(Miller 2019)
When to Seek Emergency Care
The pain may last several minutes to hours, but if it extends beyond a few hours or you should seek medical care. Blocked ducts lead to inflammation, infection and fever which can become life-threatening. (ACG 2020)
The ER will perform an ultrasound to check the size of the stones. If surgery is not required, you may be referred to a gastroenterologist—a doctor who specializes in digestive diseases—for ongoing treatment. It is important to remember that if a person has had one gallbladder attack, more episodes will likely follow.
There is no medication to treat gallstones, and surgical removal of the gallbladder is often the only option if the gallstones cannot be passed. Laparoscopic surgery is the most common surgery for gallbladder removal. A surgeon removes the gallbladder and gallstones through several small incisions in the abdomen. (Healthline 2017)
Our ER Physicians Are Ready to Diagnose Your Emergency Medical Condition
We are guided by the principle that people deserve faster, better emergency medical care than what they generally receive at a large hospital ER. Our facility offers a clean, comfortable, and friendly atmosphere when you need it most. Patients at enjoy an outstanding level of medical service provided by committed medical professionals and delivered in a prompt, efficient fashion. Our diagnostics such as labs and radiology are delivered in minutes – not hours. We are open 24/7 – 365 days to serve you quickly. When time is of the essence, choose care excellence at [FACILITY NAME].
Works Cited
Miller, Korin. “14 Signs Your Stomach Pain Is Actually a Gallbladder Attack.” SELF, 19 Aug. 2019, www.self.com/story/stomach-pain-or-gallbladder-attack.
“Gallstones in Women.” American College of Gastroenterology, 2020, gi.org/topics/gallstones-in-women/.
“Rupture of Gallbladder.” Healthline, Healthline Media, 13 Dec. 2017, www.healthline.com/health/gallbladder-rupture.
