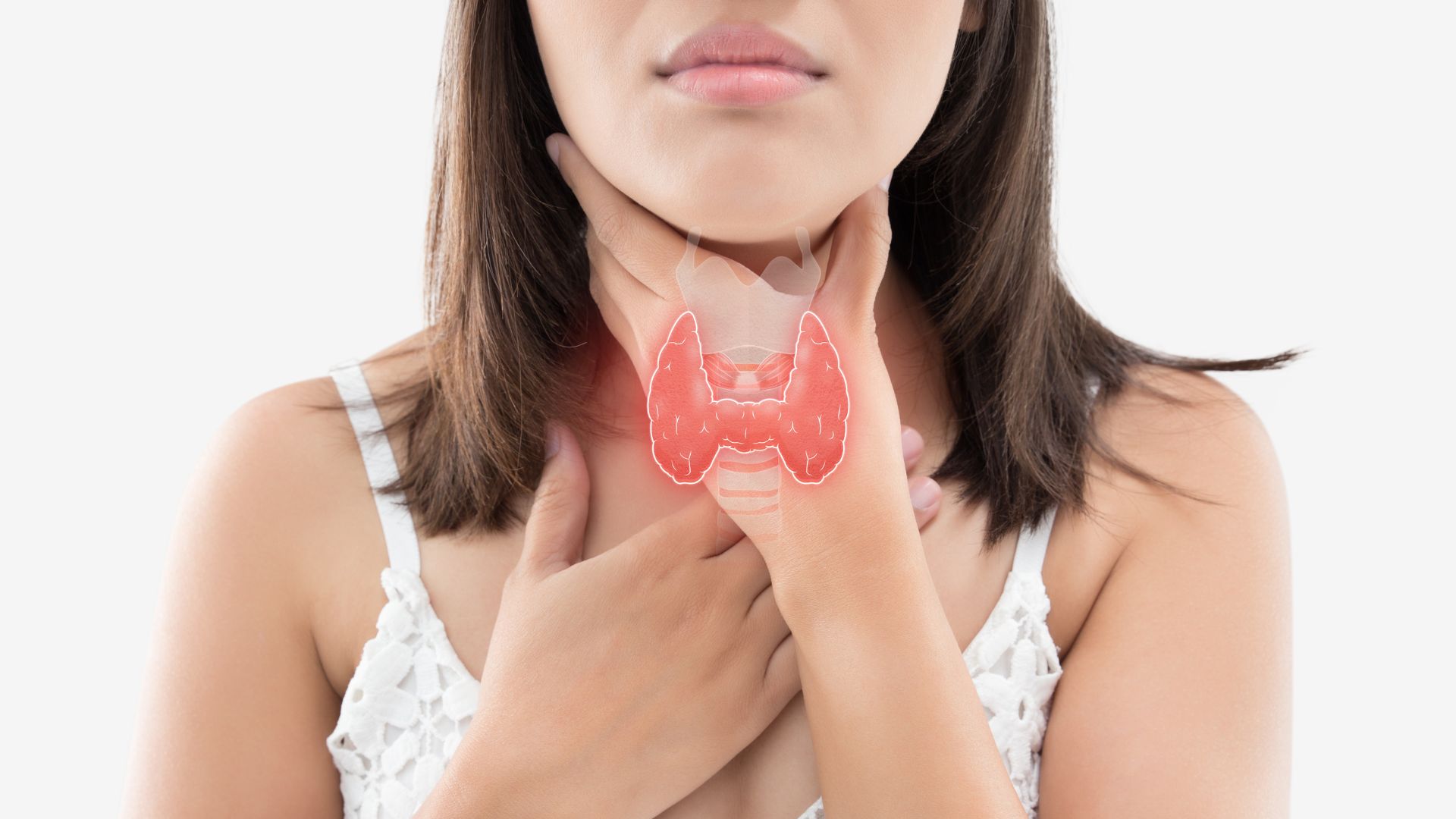
Thyroid disease is a condition that affects the thyroid, a butterfly-shaped gland in the neck. Thyroid disease can affect almost any system in the body and cause symptoms such as fatigue, weight changes, depression, and mood swings. Thyroid disease can also have serious health consequences if it is not properly diagnosed and treated. However, with early diagnosis and treatment, many people are able to manage their symptoms effectively.
The thyroid is an essential part of your overall health, playing a key role in regulating growth and development as well as metabolism. Thyroid disease occurs when there is an issue with the function or development of this important gland. Depending on what type of thyroid disease you have, it may be caused by problems with hormone production or cell signaling, or by inflammation or an autoimmune reaction.
The Purpose of the Thyroid Gland
The thyroid is responsible for producing hormones that help control various systems throughout the body, including heart rate, breathing, weight, cholesterol levels, and women’s menstrual cycles. The function and development of the thyroid gland can be affected by a variety of factors, including hormone production issues, cell abnormalities, or infections.
What to Know About Thyroid Disease
If you are experiencing symptoms such as extreme fatigue, weight changes, depression, or mood swings, it is important to talk to your doctor and be evaluated for thyroid disease. Thyroid disease can also lead to serious health issues if it is not properly diagnosed and treated. However, many people with thyroid disease are able to manage their symptoms effectively with the help of medication and lifestyle changes. If you suspect that you may be experiencing symptoms of thyroid disease, it’s important to seek medical attention right away.
Hypothyroidism Vs. Hyperthyroidism Symptoms
There are two main types of thyroid disease: hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Hypothyroidism is characterized by a sluggish or underactive thyroid gland, while hyperthyroidism is caused by an overactive thyroid.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism can include fatigue, weight gain, depression, dry skin, hair loss, and changes in your menstrual cycle. Hyperthyroidism symptoms may include insomnia, unexplained weight loss, anxiety or irritability, rapid heartbeat, or muscle weakness.
Who Gets Thyroid Disease
Thyroid disease can affect anyone — men, women, infants, teenagers and the elderly. It can be present at birth (typically hypothyroidism) and it can develop as you age (often after menopause in women).
Thyroid disease is very common, with an estimated 20 million people in the Unites States having some type of thyroid disorder. A woman is about five to eight times more likely to be diagnosed with a thyroid condition than a man.
You may be at a higher risk of developing a thyroid condition if you:
- Have a family history of thyroid disease.
- Have a medical condition (these can include pernicious anemia, Type 1 diabetes, primary adrenal insufficiency, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren’s syndrome and Turner syndrome).
- Take a medication that’s high in iodine (amiodarone).
- Are older than 60, especially in women.
- Have had treatment for a past thyroid condition or cancer (thyroidectomy or radiation).
(Cleveland Clinic, 2020)
When Thyroid Malfunction is an Emergency
If you are experiencing symptoms of thyroid storm, such as a high fever and rapid heart rate, seek medical attention immediately. This condition can be life-threatening if it is not treated promptly. Some other symptoms of thyroid storm include delirium, heart failure, and loss of consciousness. (Moore, 2018) If you have known thyroid disease and experience any of these symptoms, seek medical help right away to prevent serious complications.
Living with Thyroid Disease
Living well with thyroid disease can be a complex and challenging process, but there are several key steps that you can take to help manage your symptoms and better cope with the condition.
One of the most important things to focus on is your diet and nutrition. This means eating a healthy, balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits and vegetables, as well as lean proteins and complex carbohydrates. Additionally, you may want to consider working with a nutritionist or dietitian who can help you establish a personalized plan that takes your unique needs and symptoms into account.
Another important factor in living well with thyroid disease is managing your mental health. This may involve seeking support from a therapist or counselor, who can provide you with valuable tools and resources for self-care, as well as strategies for dealing with the emotional ups and downs that come along with managing a chronic condition (Travers, 2022).
Overall, it is important to remember that you don’t have to tackle living well with thyroid disease alone. By seeking support from your healthcare provider, nutritionists, therapists, and other resources, you can better manage your symptoms and lead a happier and healthier life.
Works Cited
Thyroid disease: Causes, symptoms, risk factors, testing and; treatment. Cleveland Clinic. (2020, April 19). Retrieved November 27, 2022, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/8541-thyroid-disease#:~:text=Thyroid%20disease%20is%20very%20common,thyroid%20condition%20than%20a%20man.
Moore, K. (2018, September 29). Thyroid storm: Causes, symptoms, and diagnosis. Healthline. Retrieved November 27, 2022, from https://www.healthline.com/health/thyroid-storm
Travers, C. (2022, May 7). Coping with thyroid disease. Verywell Health. Retrieved November 27, 2022, from https://www.verywellhealth.com/thyroid-disease-coping-4580371#:~:text=Getting%20enough%20sleep%20each%20night,weight%20caused%20by%20thyroid%20disease.
